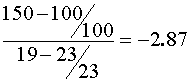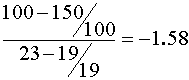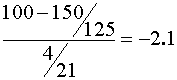Temple University
Department of Economics
Economics 52
Microeconomic Principles
Directions: You have 50 minutes to complete this exam. Write your answers on the
exam. Be sure to budget your time. You must do all of the questions. Point values are
shown. This is a closed book exam. All work must be your own. You may use your own
calculator, but no other aids are permitted.
- Problems
- (25 points) Y. Doan Giabuzoff has studied the market for infrared computer mice. She has
determined that the demand curve for such devices is
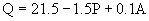 where Q is quantity, P is price and A is advertising. In the most recent year
advertising was 100. The supply curve is P=.4Q-1.
where Q is quantity, P is price and A is advertising. In the most recent year
advertising was 100. The supply curve is P=.4Q-1.
- Solve for the equilibrium price and quantity.
Demand: Q=31.5-1.5P
Supply: P=.4Q-1 or Q=2.5+2.5P
31.5-1.5P = 2.5+2.5P
P*=7.25, Q*=20.625
- Solve for producer’s surplus.
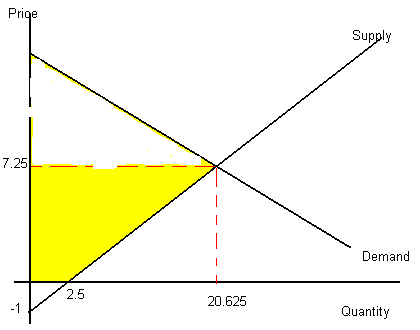
PS=(8.25)(20.625)(1/2)-(2.5)(1/2)=83.8
(25 points) Al Dente works for a firm that makes pasta. In reviewing the firm’s
accounts he has determined that his firm’s sales history is
| Year |
Quantity (cases) |
Revenue ($) |
Price/case |
| 1996 |
100 |
2300 |
23 |
| 1997 |
150 |
2850 |
19 |
- What is the elasticity of demand for his firm’s product?
Any one of three ways is acceptable:
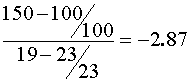
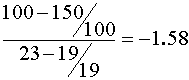
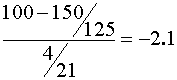
- If their goal is revenue maximization should they raise or lower the price from 1997?
Since they are in the elastic portion of the demand curve they should raise price.
- Essay
(20 points)
In your own words explain why implementing a ‘membership fee’ equal to a
buyer’s consumer surplus will not change the quantity demanded.
There will not be a change in the quantity demanded
after the imposition of a 'membership fee' because, except for the customer at the margin,
consumers are willing to pay more than the market price. The fee is only a way to collect
the difference between the market price and the price consumers are willing to pay
- Multiple Choice
(30 points)
- Production possibilities curves can be used to illustrate:
- Scarcity
- Full employment and efficiency
- Diminishing returns and increasing cost
- Opportunity costs, and choice
- All of the above
- Production possibilities frontiers shift outward when the economy's:
- Full employment level is reached
- State of technology advances
- Demand for output increases
- Productive resources are efficiently utilized
- Capital stock depreciates rapidly
- Operating inside a society's PPF is a
- way to stimulate economic growth
- result whenever the capital stock depreciates rapidly
- drawback of capitalism relative to socialism
- sign that population is outstripping the food supply
- symptom of inefficiency
- If Jill's demand price for a mountain bike exceeds the $500 price tag, then
- Jill will purchase the bike
- Mountain bikes are an inferior good
- Jill will not purchase the bike
- Mountain bikes are a normal good
- Surpluses of mountain bikes are likely
- When demand increases, the demand curve shifts
- down and to the left
- in a clockwise rotation
- up and to the right
- counterclockwise
- none of the above
- A demand curve would not shift if there were changes in the
- tastes and preferences of consumers
- size or distribution of national income
- price of the good
- number or age composition of buyers
- expectations of consumer's about availability
- Demand is positively related to income for
- inferior goods
- normal goods
- complementary goods
- joint products
- substitute goods
- If price cuts in video recorders cause expanded cable TV hookups, these are
- luxury goods
- substitute goods
- normal goods
- inferior goods
- complementary goods
- Market prices that are below equilibrium tend to create
- surpluses of the good
- declines in resource costs
- pressures for research and development
- shortages of the good
- buyers' markets
- There is a discovery of a vast new oil field. The impact on the equilibrium price and
quantity in the market for gasoline will be
- higher price and lower quantity
- lower price and lower quantity
- higher price and higher quantity
- higher price and lower quantity
- lower price and greater quantity
- It is learned that a glass of red wine each day can reduce the likelihood of heart
attack. The impact on the equilibrium price and quantity in the market for seltzer water
will be
A. higher price and lower quantity
- lower price and lower quantity
- higher price and higher quantity
- higher price and lower quantity
- lower price and greater quantity
- As price falls and quantity demanded rises along a negatively sloped linear demand curve
- total revenue falls up to the point where elasticity equals zero, thereafter it rises
- the price elasticity of demand decreases
- there is a contradiction to the law of supply
- the incentive for substituting away from the good rises
- a constant slope ensures a fixed elasticity
- Cross-price elasticities of demand are probably most positive for
- shoe repairs and new shoes
- syrup and waffles
- gasoline and limousines
- college tuition and textbooks
- coal and iron
- National income booms from $3.75 trillion to $4.25 trillion and new car sales rise from
3 million to 5 million cars annually. The income elasticity of demand for cars is
- .5
- 1.0
- 2.0
- 3.0
- 4.0
If you use the 'mid-point' formula you will get this answer.
- Profitability of firms falls, thereby reducing their ability to pay dividends. The
demand for investment grade bonds will
- decrease
- increase
- remain the same
- none of the above.