October 8, 1998
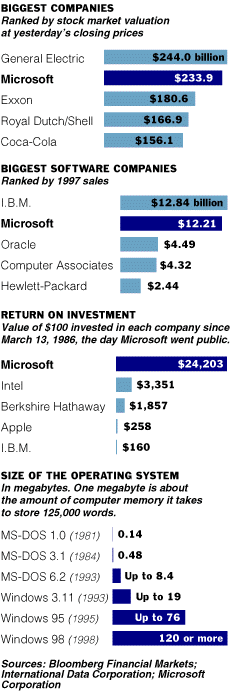
From a tiny startup in 1975, Microsoft has risen to become the dominant force in the personal computer industry, largely because of two fundamental insights shared by the company's co-founders, William H. Gates and Paul G. Allen. The first was that software was a promising business on its own rather than something included with the machine. The second stroke of business brilliance was recognizing the extraordinary wealth and industry influence that the company could grasp as the owner of the industry-standard operating system. Its Windows operating system business has given Microsoft the money and the market power to move into an array of other businesses, from spreadsheets and Internet software to electronic commerce and cable television.
MARKET SHARE
THE OPERATING SYSTEMWHAT IT IS The essential software that enables computer programs to control hardware.
WHAT HAPPENED When I.B.M. designed its PC in 1981, Microsoft won the contract to supply the operating system. To fill the contract, it bought an existing operating system from a Seattle company for $25,000, made a few modifications and renamed it MS-DOS. In 1984, after Apple introduced the Macintosh, Microsoft began developing a graphical interface to make DOS easier to use. In 1992, it abandoned development with I.B.M. of an operating system, OS/2, choosing instead to develop its Windows into a family of integrated operating systems for different kinds of machines: Windows 95/98 is the industry standard, Windows NT is fast becoming one, and Windows CE is trailing.
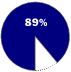
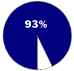
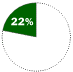
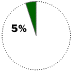
Based on number of personal computer operating systems sold in 1997Windows 95/98 OPERATES Personal computers
COMPETITION Apple
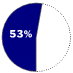
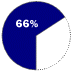
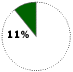
Based on number of workstation systems shipped in the first quarter of 1998Windows NT OPERATES Workstations and large servers for networking
COMPETITION I.B.M., Sun Microsystems, Hewlett-Packard, Novell
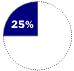
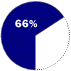
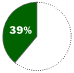
Based on number of systems in handheld devices sold in 1997Windows CE OPERATES Handheld computers, consumer electronics devices
COMPETITION Palm Computing (a division of 3Com)
INTERNET
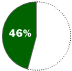
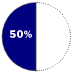
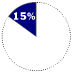
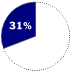
Browsers in use in 1998Browser WHAT IT IS Software for viewing and navigating the World Wide Web.
WHAT HAPPENED Microsoft built its Internet Explorer browser on software licensed from Spyglass Inc. Trailing the market leader, Netscape Navigator, Microsoft folded its browser into its operating system and gave it away free. Its tactics in this market prompted the current antitrust suit.
COMPETITION Netscape
WHAT IT IS Software for sending and receiving electronic messages over the Internet.
WHAT HAPPENED In Windows 95, Inbox, a feature that combined fax software and e-mail, proved unpopular. An improved, free product, Outlook Express, is gaining, as is the e-mail product shipped as part of Outlook, a personal information manager, including a scheduler and address book.
COMPETITION Eudora by Qualcomm and cc:mail by Lotus
TCP/IP Protocol
WHAT IT IS The communication rules of the Internet.
WHAT HAPPENED Beginning with Windows 95, it built the TCP/IP protocol into its operating system. This effectively destroyed the business of small developers of Winsocks, the software that enables TCP/IP in Windows.
COMPETITION None
Based on 1997 dollar salesWeb Authoring Tools WHAT THEY ARE Software for producing Web pages
WHAT HAPPENED Acquired Vermeer Technologies, maker of the Frontpage Web authoring tool. It now markets a full-featured version and ships a rudimentary version as part of Windows 98.
COMPETITION Pagemill by Adobe Systems, Filemaker by Apple Computer, Visual Page by Symantec
UTILITIESWHAT THEY ARE Software that performs maintenance, diagnostics or repairs on computer hardware or software.
WHAT HAPPENED Incorporated in its operating systems features similar or identical to those of Norton Utilities, and other companies. Competition eroded quickly after 1991, when Microsoft added many of the most popular utilities to DOS 5.0. When Microsoft added compression software that doubled the capacity of hard drives, the market leader in compression software sued for patent infringement and won.
COMPETITION Norton Utilities by Symantec and Nuts and Bolts by McAfee
OFFICE SUITE
Based on 1997 dollar salesOffice Suite WHAT IT IS A collection of software applications that can share data.
WHAT HAPPENED In 1989, Microsoft bundled Word and Excel for the Macintosh with other business applications and sold them under the name Office. Its success led to a DOS version the following year, and then versions for Windows. Different versions of Office are sold for several kinds of businesses.
COMPETITION SmartSuite by Lotus, Wordperfect Suite by Corel
Based on 1997 dollar salesPresentation Software WHAT IT IS Software for creating business presentations on computer screens.
WHAT HAPPENED In 1987, Microsoft acquired Forethought, the maker of Powerpoint, a leader in presentation software, and increased its market share considerably by including Powerpoint in its Office suite.
COMPETITION Visio
Based on number in use, end of 1997Word Processing WHAT IT IS Software for creating text documents.
WHAT HAPPENED Word was introduced in 1983, but made little progress against the early leader, WordStar, and later against WordPerfect, which dominated the market for seven years until it failed to develop a timely version for Windows. Word is now the leading word processor.
COMPETITION WordPerfect by Corel, WordPro by Lotus
Based on number in use, end of 1997Spreadsheet WHAT IT IS Software for analyzing and modeling financial data.
WHAT HAPPENED Though Microsoft's first spreadsheet, Multiplan, got glowing reviews when introduced in 1982, it failed to compete with Lotus 1-2-3. In 1985, Microsoft tried again with Excel for the Macintosh and added Excel for Windows in 1987. It is now the world's leading spreadsheet.
COMPETITION 1-2-3 by Lotus, Quattro Pro by Corel
NEW MEDIA
Among guide sites, based on number of user visits during August
- City Guides
WHAT IT IS An online service that offers information about a specific city or region.
WHAT HAPPENED In 1997, it opened its first Sidewalk city guide, in Seattle, followed by Sidewalks in New York and nine other cities: Boston, Denver, Houston, Minneapolis-St. Paul, San Diego, San Francisco, Sydney and Washington.
COMPETITION CitySearch, America Online's Digital City and Zip2
Based on online bookings in 1997
- Electronic Commerce
WHAT IT IS Web sites that generate revenue through online sales of products or services
WHAT HAPPENED Its Carpoint enables users to research new and used vehicles, compare prices and arrange purchases. Expedia travel agency enables users to research and book reservations for airlines, hotels, car rentals and cruises.
COMPETITION Travelocity, which is operated by Sabre Group and Autobytel.com
- Online Publishing
WHAT IT IS Publishing on the Internet.
WHAT HAPPENED Started MSN, an online service. Also started MSN.com, a Web site. Joined with NBC to form MSNBC, a cable television and Web channel for news and information. Launched Slate, an online magazine.
COMPETITION America Online, TV networks that have Web components and Web "zines" like Salon and Feed.
Based on 1997 dollar sales
- Multimedia Publishing
WHAT IT IS Computer software that combines text with video, animated graphics and sound.
WHAT HAPPENED Microsoft created Encarta, a multimedia encyclopedia around the Funk and Wagnall's print version in 1993. It is now the world's best-selling encyclopedia, far surpassing sales of print encyclopedias.
COMPETITION Britannica, Compton's and World Book
DATABASE MANAGEMENT
Based on 1997 dollar salesWHAT IT IS Software for storing, manipulating and accessing large amounts of data. WHAT HAPPENED After stumbling in the database market against Ashton Tate's dBase for years, Microsoft in 1992 acquired Fox Software, whose FoxPro ran dBase programs faster than dBase ran them. Microsoft markets Access, a simpler data base, with its Office suite, and it developed its SQL Server data base for NT.
COMPETITION Oracle, I.B.M., Sybase, Inprise, Computer Associates
MULTIMEDIA
Based on 1997 dollar salesWHAT IT IS Software that enables audio and video content on computers. WHAT HAPPENED Microsoft is pushing hard into the market for "streaming" technologies that enable sound and video over the Web. Its complete multimedia product, Netshow, requires Web sites to use Windows NT server software. A less ambitious effort, Windows Media Player, aggregates the audio and video products of other companies. Microsoft bought one competitor, Xtreme, and invested in Real Networks and VDOnet.
COMPETITION Real Networks.
PERSONAL FINANCE
Based on 1997 dollar salesWHAT IT IS Software to manage household finances. WHAT HAPPENED Introduced its personal finance software, Microsoft Money, in 1991 and four years later tried to buy its major competitor, Intuit, which produces the industry-leading Quicken financial software. The Intuit deal was dropped after the Government threatened antitrust action.
COMPETITION Intuit, various proprietary electronic banking packages.
Sources: Dataquest; International Data Corporation; Jupiter Communications; PC Data; Zona Research; Media Metrix
New York Times, 1/8/99