Page 1
1. The idea that consumers ultimately dictate what will be produced by choosing what to purchase is known as
a. laissez-faire.
b. the economic problem.
c. centralized decision making.
d.* consumer sovereignty.
2. The services provided by a public school system are
a. a public good, since tax dollars pay for the services provided.
b.* not a true public good, because students could be prevented from receiving these services if they did not pay for them.
c. a public good, because a free market would not produce educational services.
d. not a public good, because the quality of educational services varies among school districts.
3. In terms of the production possibility frontier, an increase in productivity attributable to new technology would best be shown by
a. a movement along the frontier.
b.* the production possibility frontier shifting up and to the right.
c. a movement from a point inside the frontier to a point on it.
d. a movement toward the origin.
4. An improvement in technology will cause
a.* the production possibility frontier to shift up and to the right.
b. the production possibility frontier to shift back and to the left.
c. the economy to move down the production possibility frontier.
d. the economy to move closer to its production possibility frontier.
Page 2

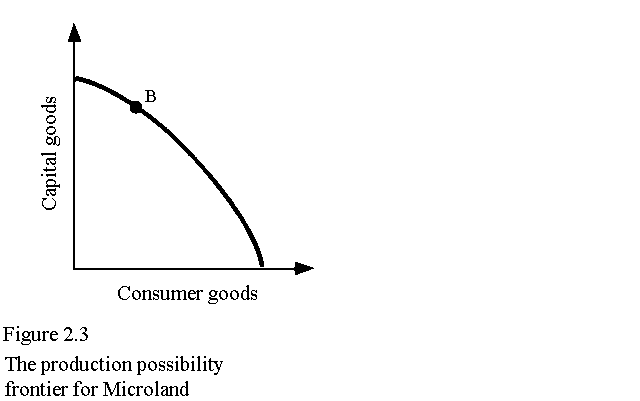
5. Refer to Figure 2.3. A point like point B represents a situation of
a. full employment but production inefficiency.
b. less than full employment but production efficiency.
c.* both full resource employment and production efficiency.
d. less than full employment and production inefficiency.
Page 3
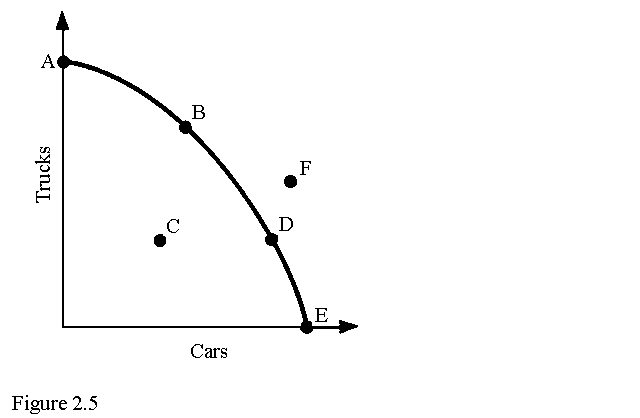
6. According to Figure 2.5, the point where only cars are produced is
a. A.
b. B.
c. C.
d.* E.
7. Refer to Figure 2.5. The economy moves from point B to point D. This could be explained by
a. a reduction in unemployment.
b. an improvement in technology.
c. an increase in economic growth.
d.* a change in society's preferences for cars versus trucks.
8. The process of using resources to produce new capital is
a. research and development.
b.* investment.
c. consumption.
d. economic growth.
Page 4
9. The basic coordinating mechanism in a free market system is
a. quantity.
b.* price.
c. a central government authority.
d. the corporation.
10. Which of the following is TRUE of a market economy?
a. Private firms make a profit selling public goods.
b.* Monopolies can develop.
c. Innovation and new production are discouraged.
d. Inefficient producers have greater protection than in a command economy.
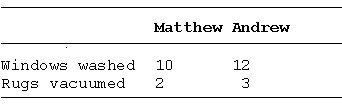
11. Refer to the above table. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
a. Matthew has a comparative advantage in both washing windows and vacuuming rugs.
b. Andrew has a comparative advantage in both washing windows and vacuuming rugs.
c. Matthew has a comparative advantage in vacuuming rugs and Andrew has a comparative advantage in washing windows.
d.* Andrew has a comparative advantage in vacuuming rugs and Matthew has a comparative advantage in washing windows.
12. Economic growth may occur when
a. a society acquires new resources.
b. a society learns to produce more using existing resources.
c. the society begins to produce the combination of goods society wants most.
d.* both a and b.
Page 5
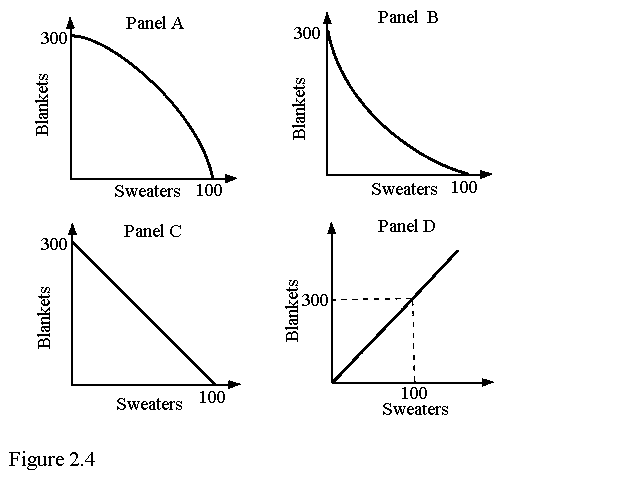
13. Refer to Figure 2.4. Assume that in Microland the marginal rate of transformation of sweaters for blankets is constant and equal to -3. A graph of this society's production possibility frontier will be represented by
a. A.
b. B.
c.* C.
d. D.
14. The concept of choice would become irrelevant if
a. we were dealing with a very simple, one-person economy.
b. poverty were eliminated.
c.* scarcity were eliminated.
d. capital were eliminated.
Page 6
15. An economy that is producing at the wrong point on its production possibility frontier is
a. efficient, since it is on the production possibility frontier.
b.* inefficient, since the combination of goods and services produced is not what people want.
c. efficient, since the economy is producing goods at the lowest possible cost.
d. inefficient, since that combination of goods could be produced at a lower cost if more efficient technology were employed.
16. Economic growth shifts a society's production possibility frontier up and to the right.
a.* True
b. False
17. Public goods are those goods and services that are consumed by governmental bodies.
a. True
b.* False
18. The "economic problem" is that given scarce resources, how do large societies go about answering the basic economic questions of what will be produced, how it will be produced, and who will get it.
a.* True
b. False
19. The resulting unemployment from the recession of the early 90s corresponds to points outside our society's production possibility frontier.
a. True
b.* False
20. Things that have already been produced that are in turn used to produce other goods and services over time are called "capital."
a.* True
b. False
Page 1
1. d 38
2. b 40
3. b 35
4. a 35
5. c 31
6. d 31
7. d 31
8. b 30
9. b 40
10.b 40
11.d 28
12.d 34
13.c 33
14.c 27
15.b 32
16.True 35
17.False 40
18.True 36
19.False 32
20.True 25